How it works:
According to Einstein’s general theory of relativity, time and space are merged into one quantity called spacetime. Under this theory, massive objects cause space-time to bend, and gravity is simply the bending of space-time. When light moves through spacetime, the theory predicts that the path of light is also bent by the mass of an object. Gravitational lensing is an observable example of the application of Einstein’s theory.
Einstein ring:
This phenomenon was predicted by Albert Einstein already in 1915 in his General Theory of Relativity. The Einstein ring is a ring of electromagnetic radiation from a distant object, created by the gravitational effect of a galaxy in the foreground.

Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA under CC BY 4.0
Animation (Credit: NASA):
This video is integrated via the Video.cab service. To play it, click the “Show content” button. This will share data with the third-party provider. More information in our privacy policy.
Microlensing – a special type of gravitational lensing
The microlensing method finds planets by the effect of their gravity on light coming to Earth from a more distant background star. The brightness variations of the background star can be used to infer the existence of a planet, even if no light is measured directly from the planet or its central star.

Schematic illustration of the microlensing method. Left: Lens star in the foreground moves past a background star. Through gravitational lensing, the background star’s light is collected and therefore amplified, while the lens star is in front of it. Right: If the lens star is orbited by a planet, the planet’s gravitation also influences the light and there is a short-time additional amplification of the background star’s light. Credit: ESA
This video is integrated via the Video.cab service. To play it, click the “Show content” button. This will share data with the third-party provider. More information in our privacy policy.
The first microlensing event:
In July 2003, the first exoplanet was found via microgravity lensing effect. OGLE-2003-BLG-235L is located in the constellation Sagittarius and orbits an orange dwarf star. Read more about it here.
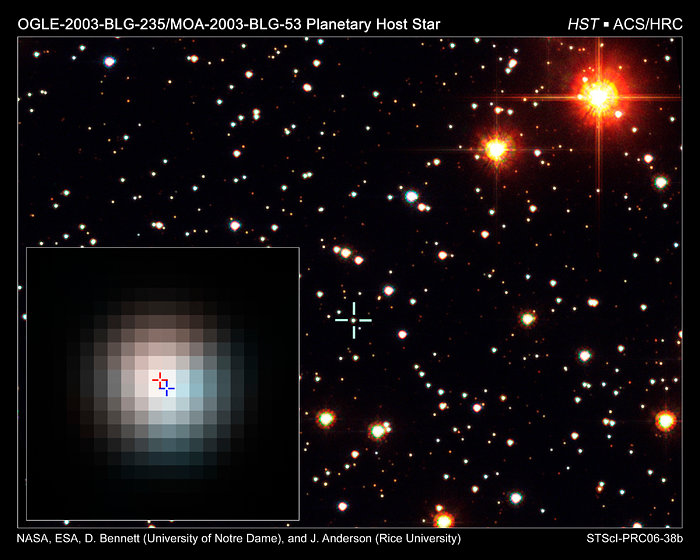
Credit: NASA / ESO
Interesting questions on the topic:
Q: What parameters are obtained by microlensing?
A: From the measurements one can read the ratio between the mass of the planet and that of its star. Furthermore, one gets the separation between the planet and its host star at the time of the observation .
Q: What is the difference between gravitational lensing and microlensing?
A: Gravitational lensing is caused by a huge object like a galaxy. Microlensing is a special case of gravitational lensing where the lens is a star within our own galaxy.
Recommended books to the topic:

Gravitational Lenses
P. Schneider, J. Ehlers, E. E. Falco
Publisher: Springer Verlag
ISBN: 9780387970707

Introduction to Gravitational Lensing: With Python Examples
Massimo Meneghetti
Publisher: Springer Verlag
ISBN: 978-3-030-73582-1
Find more books to the topic exoplanets and astronomy for children, amateurs and scientists in our booklist.
